Chronic Hep B and the Liver

What is HEP B?
Chronic hepatitis B (hep B) is caused by a long-term infection of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Over time, it can lead to serious liver damage.
What does the liver do?
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body.
You cannot survive without your liver because it has many important jobs.
Some things your liver does are:
Fight Off Infection
Help Digest Food

Store Energy
And Nutrients
Remove Harmful
Chemicals From
Your Blood
How HEP B affects the liver
Chronic HEP B can lead to:
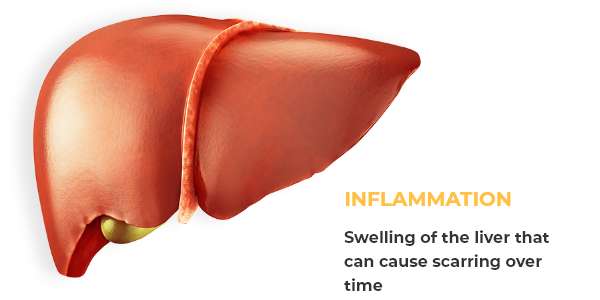
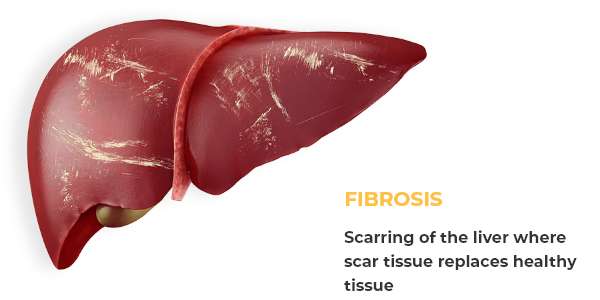
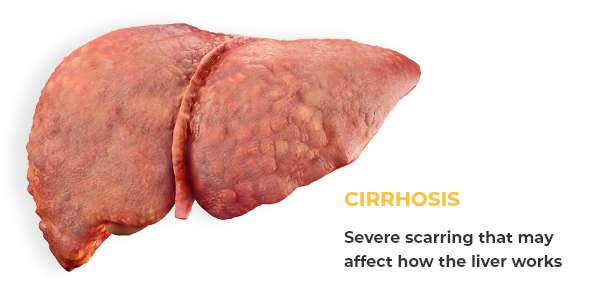
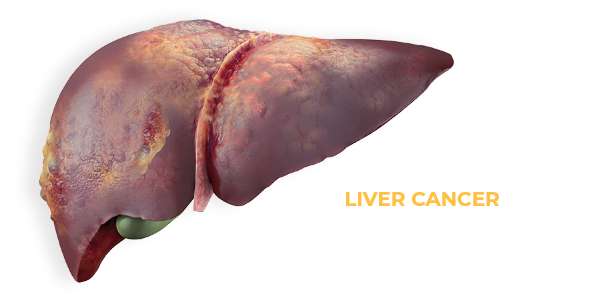
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms of a hep B infection may include:

Tiredness / Fatigue

Joint Pain

Stomach Pain

Fever

Nausea & Vomiting

Loss Of Appetite

Jaundice
(Yellowish Eyes And Skin)

Light-Colored
Stools/Dark Urine
- It's important to know that if you have chronic hep B, you may not experience any symptoms. Even if you don't feel any symptoms, the hep B virus is still in your body and may be harming your liver.
The goal of treatment
With hep B, the amount of HBV in your body (viral load) can go up or down.
The higher your viral load, the higher the risk for you to develop liver damage.
That’s why it’s important to visit your doctor regularly so he or she can monitor your liver health.
The goal of prescription medicine is to:
- Decrease The Amount Of Virus In The Body
- Reduce The Risk Of Liver Damage
History of chronic HEP B treatment
Timeline of FDA Approvals: Oral Antiviral Treatments for Chronic Hep B
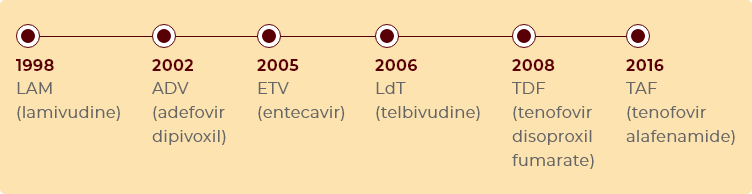
This timeline is not intended to compare the efficacy or safety of the products listed above.
Tafsafe is the first treatment for chronic hep B approved since TDF in 2008. Talk to your doctor to determine which treatment is right for you.

